Cancers, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 06 julho 2024
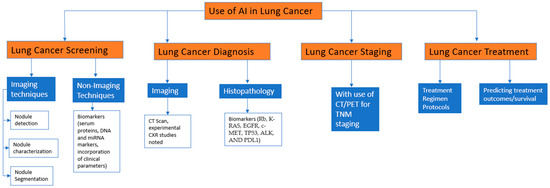
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, emphasizing the need for improved diagnostic and treatment approaches. In recent years, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) has sparked considerable interest in its potential role in lung cancer. This review aims to provide an overview of the current state of AI applications in lung cancer screening, diagnosis, and treatment. AI algorithms like machine learning, deep learning, and radiomics have shown remarkable capabilities in the detection and characterization of lung nodules, thereby aiding in accurate lung cancer screening and diagnosis. These systems can analyze various imaging modalities, such as low-dose CT scans, PET-CT imaging, and even chest radiographs, accurately identifying suspicious nodules and facilitating timely intervention. AI models have exhibited promise in utilizing biomarkers and tumor markers as supplementary screening tools, effectively enhancing the specificity and accuracy of early detection. These models can accurately distinguish between benign and malignant lung nodules, assisting radiologists in making more accurate and informed diagnostic decisions. Additionally, AI algorithms hold the potential to integrate multiple imaging modalities and clinical data, providing a more comprehensive diagnostic assessment. By utilizing high-quality data, including patient demographics, clinical history, and genetic profiles, AI models can predict treatment responses and guide the selection of optimal therapies. Notably, these models have shown considerable success in predicting the likelihood of response and recurrence following targeted therapies and optimizing radiation therapy for lung cancer patients. Implementing these AI tools in clinical practice can aid in the early diagnosis and timely management of lung cancer and potentially improve outcomes, including the mortality and morbidity of the patients.
Cancer Awareness Word Search – Free Printable
O Amar Mota Bou Get File - Colaboratory

Cancer

Cancer Facts & Figures 2023

Multi-omics integrated circulating cell-free DNA genomic signatures enhanced the diagnostic performance of early-stage lung cancer and postoperative minimal residual disease - eBioMedicine

The global burden of cancer attributable to risk factors, 2010–19: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019 - The Lancet
from Flow Cytometry to Cytomics, Page 2

Mother find out dying child is cancer free ❤️, cancer free
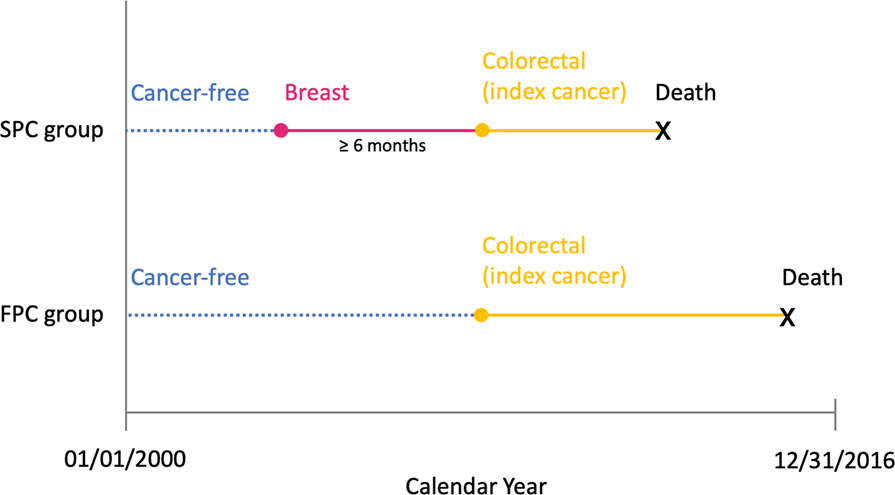
Mortality after second malignancy in breast cancer survivors compared to a first primary cancer: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study

Remission, cancer-free, no evidence of disease: What's the difference?

What is cancer of unknown primary (CUP)?
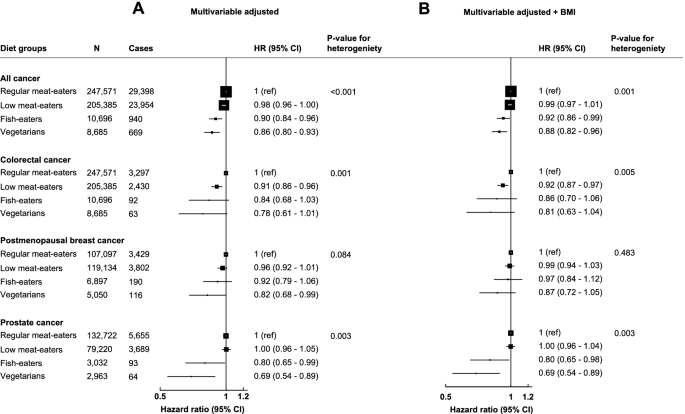
Risk of cancer in regular and low meat-eaters, fish-eaters, and vegetarians: a prospective analysis of UK Biobank participants, BMC Medicine
Recomendado para você
-
 PAPA'S GAMES 🍔 - Play Online Games!06 julho 2024
PAPA'S GAMES 🍔 - Play Online Games!06 julho 2024 -
Retro Goal Unblocked Poki06 julho 2024
-
 Papa's Sushiria - Play Papa's Sushiria Game online at Poki 206 julho 2024
Papa's Sushiria - Play Papa's Sushiria Game online at Poki 206 julho 2024 -
PAPA'S CHEESERIA (DAY 56) #papascheeseria #papasgames #papasgameplay06 julho 2024
-
 TOP 10 BEST Cheap Eats in Avondale, AZ - November 2023 - Yelp06 julho 2024
TOP 10 BEST Cheap Eats in Avondale, AZ - November 2023 - Yelp06 julho 2024 -
 Papa's Parkeria, Flipline Studios Fanon Wiki06 julho 2024
Papa's Parkeria, Flipline Studios Fanon Wiki06 julho 2024 -
actually getting to rank 10 on a papa's game Part 5 #poofesure #papasc06 julho 2024
-
 Atlantic Ave Magazine April 202206 julho 2024
Atlantic Ave Magazine April 202206 julho 2024 -
 THE BEST 10 Restaurants near HAVRE DE GRACE, MD 21078 - Last Updated December 2023 - Yelp06 julho 2024
THE BEST 10 Restaurants near HAVRE DE GRACE, MD 21078 - Last Updated December 2023 - Yelp06 julho 2024 -
San Clemente Pizza Co Menu06 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
Ocean Toes Bookkeeping06 julho 2024
-
 GRID Autosport - Playstation 3 Black Edition : Namco06 julho 2024
GRID Autosport - Playstation 3 Black Edition : Namco06 julho 2024 -
 11,606 Anime Girl Poses Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors06 julho 2024
11,606 Anime Girl Poses Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors06 julho 2024 -
 Does Grand Theft Auto 6 deliver the generational leap we were06 julho 2024
Does Grand Theft Auto 6 deliver the generational leap we were06 julho 2024 -
 Otoyomegatari06 julho 2024
Otoyomegatari06 julho 2024 -
 Busco Jugadores Técnicos para un Host de pago en Minecraft Java 1.18.1. Todo interesado puede comentar en este post, o en su defecto enviarme mensaje privado por reddit Estaré dejando el server06 julho 2024
Busco Jugadores Técnicos para un Host de pago en Minecraft Java 1.18.1. Todo interesado puede comentar en este post, o en su defecto enviarme mensaje privado por reddit Estaré dejando el server06 julho 2024 -
 Fox McCloud Returns As Star Fox 64 3D Launches Worldwide06 julho 2024
Fox McCloud Returns As Star Fox 64 3D Launches Worldwide06 julho 2024 -
 Nemu, Tensei Shitara Slime Datta Ken Wiki06 julho 2024
Nemu, Tensei Shitara Slime Datta Ken Wiki06 julho 2024 -
 Lass, Wiki06 julho 2024
Lass, Wiki06 julho 2024 -
 The Super Mario Bros. Movie' Directors Explain Changes to Princess Peach06 julho 2024
The Super Mario Bros. Movie' Directors Explain Changes to Princess Peach06 julho 2024


