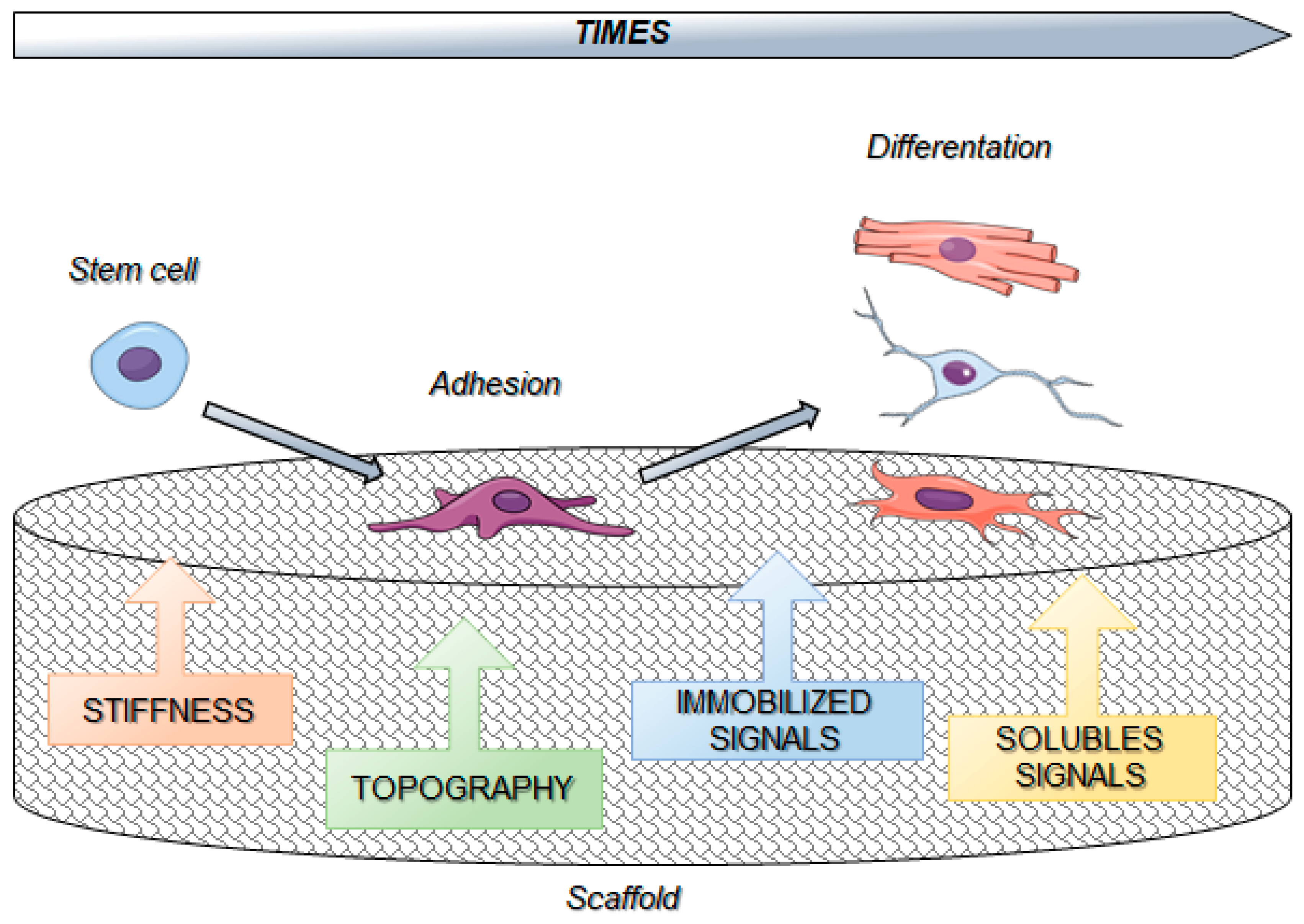
Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 05 julho 2024

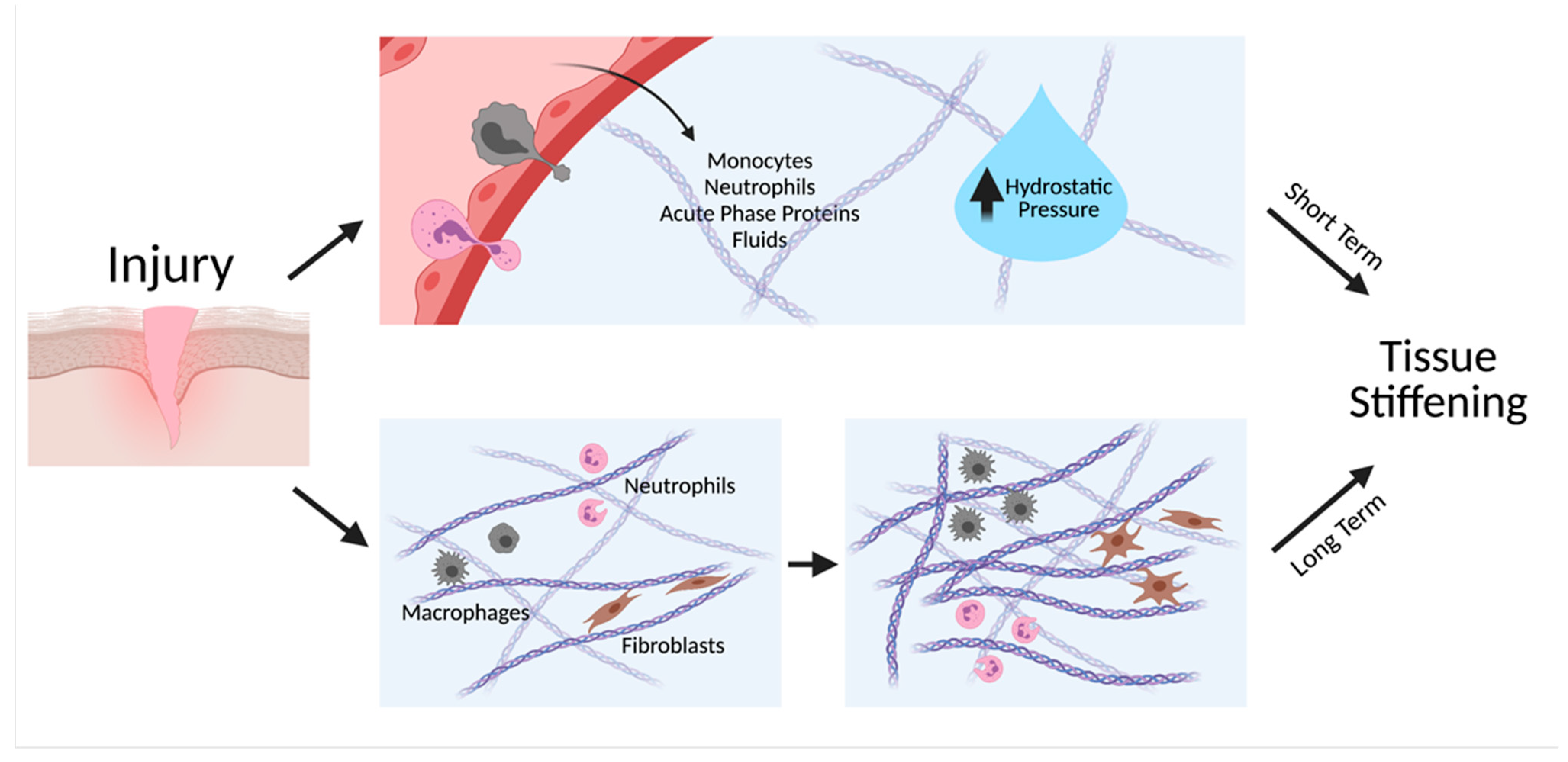
Cells, Free Full-Text

Cell Shape and Durotaxis Explained from Cell-Extracellular Matrix Forces and Focal Adhesion Dynamics - ScienceDirect
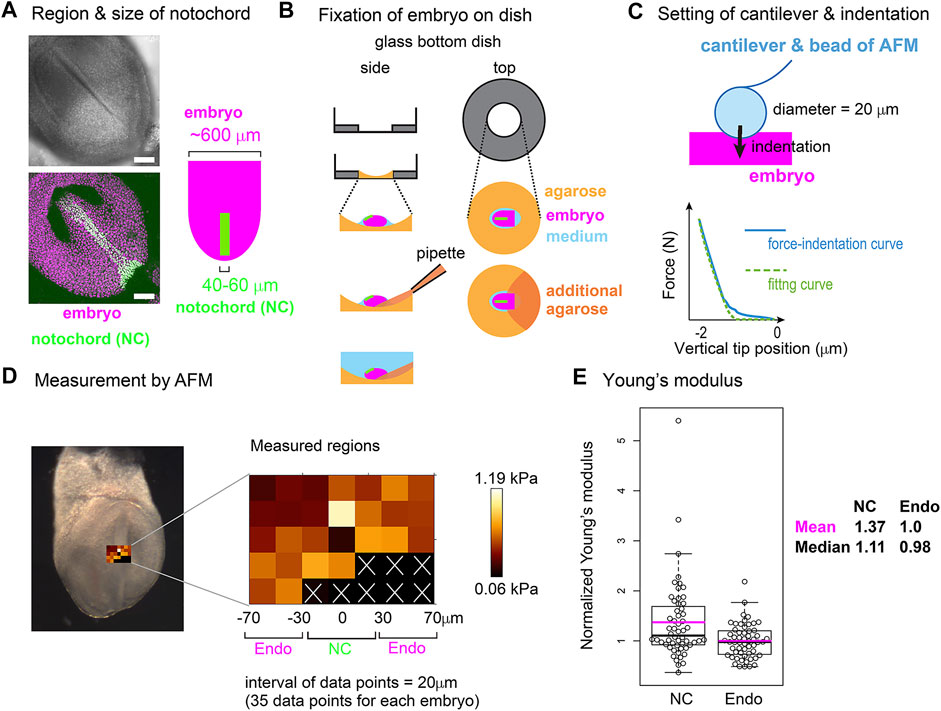
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface
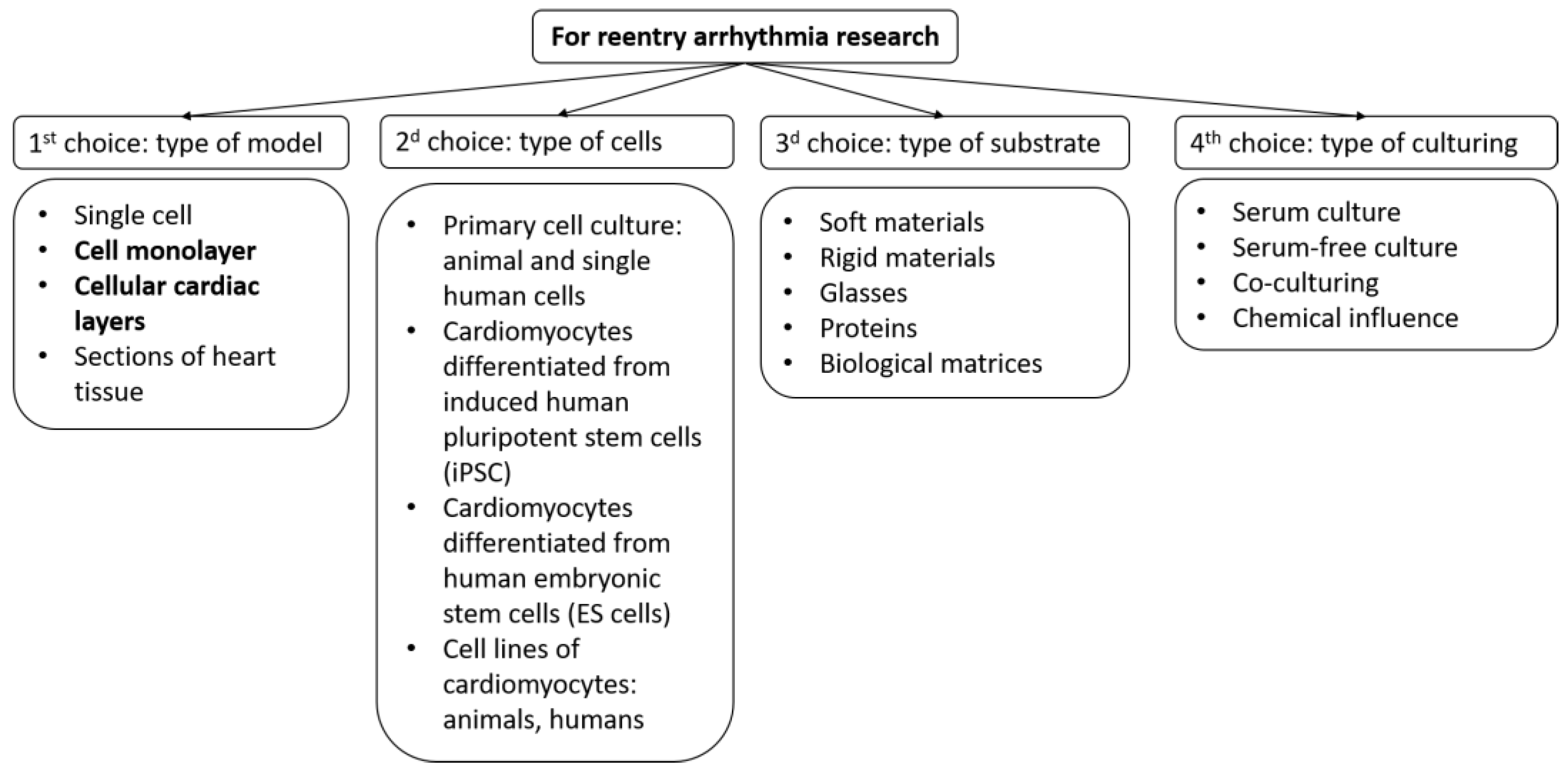
Biomimetics, Free Full-Text

PDF) Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

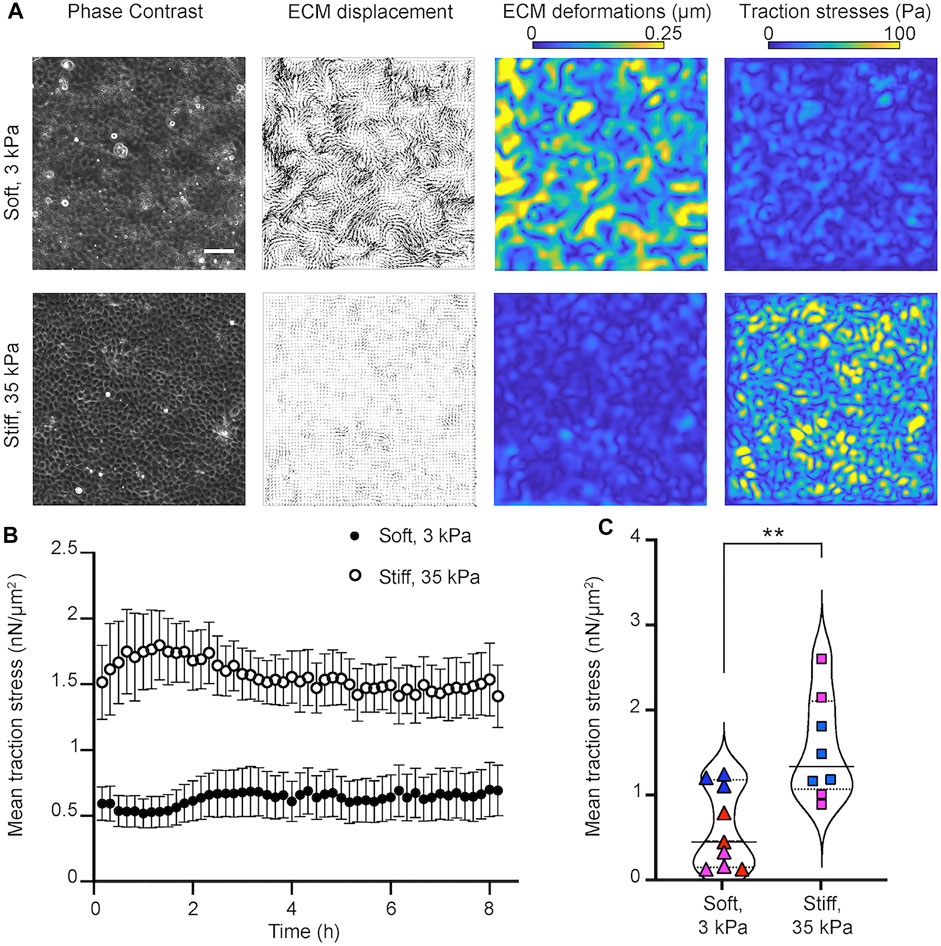
Physicochemical Tools for Visualizing and Quantifying Cell-Generated Forces
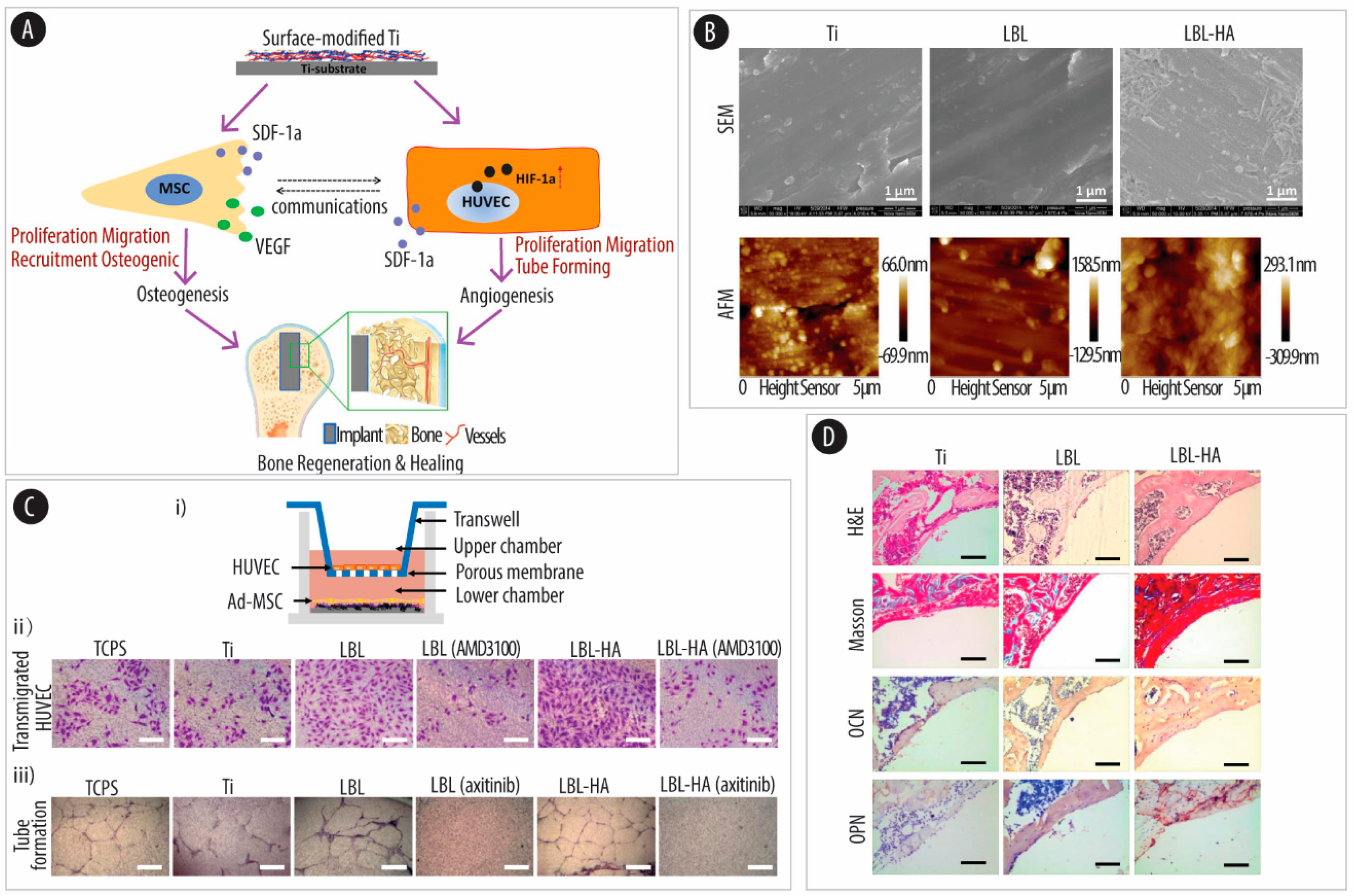
Nanomaterials, Free Full-Text
Cells, Free Full-Text
Frontiers A Stiff Extracellular Matrix Favors the Mechanical Cell Competition that Leads to Extrusion of Bacterially-Infected Epithelial Cells

Cellular segregation in cocultures is driven by differential adhesion and contractility on distinct timescales
Recomendado para você
-
 U played (jessie murph cover;djons prod.remix) (TIK TOK)05 julho 2024
U played (jessie murph cover;djons prod.remix) (TIK TOK)05 julho 2024 -
 Squishy literally gave me his old jersey at NARLI THIS is what makes him, and Rocket League so great. Go Cloud 9!!! : r/RocketLeague05 julho 2024
Squishy literally gave me his old jersey at NARLI THIS is what makes him, and Rocket League so great. Go Cloud 9!!! : r/RocketLeague05 julho 2024 -
 Japan Molang Squishy05 julho 2024
Japan Molang Squishy05 julho 2024 -
 DURGOD Taurus K310 Big Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - 104 Keys - Double Shot PBT - NKRO - USB Type C (Cherry Brown,Black,ANSI/US) : Video Games05 julho 2024
DURGOD Taurus K310 Big Mechanical Gaming Keyboard - 104 Keys - Double Shot PBT - NKRO - USB Type C (Cherry Brown,Black,ANSI/US) : Video Games05 julho 2024 -
 YupYay 4 Pack Custom OEM R4 Keycaps PBT Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps Cute Cat Paw Key Cap Kawaii Gaming Keycaps for Mechanical Keyboard with Keycap Puller (White Base) : Electronics05 julho 2024
YupYay 4 Pack Custom OEM R4 Keycaps PBT Mechanical Keyboard Keycaps Cute Cat Paw Key Cap Kawaii Gaming Keycaps for Mechanical Keyboard with Keycap Puller (White Base) : Electronics05 julho 2024 -
 A Synergistic Workspace for Human Consciousness Revealed by Integrated Information Decomposition05 julho 2024
A Synergistic Workspace for Human Consciousness Revealed by Integrated Information Decomposition05 julho 2024 -
 Sanrioed My Melody Kuromi Cinnamoroll Christmas Look Keyboard Cap Cross Shaft Mechanical Keyboard Base Translucent ChristmasGift05 julho 2024
Sanrioed My Melody Kuromi Cinnamoroll Christmas Look Keyboard Cap Cross Shaft Mechanical Keyboard Base Translucent ChristmasGift05 julho 2024 -
 Conjunto Com 2 Stwhack-a-mole Eletrônico Minijogo Portátil Para Crianças Com Design De Desenhos Animados Em Várias Cores - Pingente De Chaveiro05 julho 2024
Conjunto Com 2 Stwhack-a-mole Eletrônico Minijogo Portátil Para Crianças Com Design De Desenhos Animados Em Várias Cores - Pingente De Chaveiro05 julho 2024 -
 Rii i8+ Mini Bluetooth Keyboard with Touchpad&QWERTY Keyboard, Backlit Portable Wireless Keyboard for Smartphones laptop/PC/Tablets/Windows/Mac/TV/Xbox/PS3/Raspberry Pi.Green : Electronics05 julho 2024
Rii i8+ Mini Bluetooth Keyboard with Touchpad&QWERTY Keyboard, Backlit Portable Wireless Keyboard for Smartphones laptop/PC/Tablets/Windows/Mac/TV/Xbox/PS3/Raspberry Pi.Green : Electronics05 julho 2024 -
 3.21 Crucible - Dying on Frost Blades? FIX IT! Day 3 update/tips05 julho 2024
3.21 Crucible - Dying on Frost Blades? FIX IT! Day 3 update/tips05 julho 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Block Square Puzzle Android game - Mod DB05 julho 2024
Block Square Puzzle Android game - Mod DB05 julho 2024 -
 CapCut_stands awakening discord05 julho 2024
CapCut_stands awakening discord05 julho 2024 -
 Personagem de desenho animado de gota de água azul com raiva05 julho 2024
Personagem de desenho animado de gota de água azul com raiva05 julho 2024 -
 LIKO MEETS ROY. Pokémon Horizons05 julho 2024
LIKO MEETS ROY. Pokémon Horizons05 julho 2024 -
 The Big Feelings of the Sugar Apple Fairy Tale Anime05 julho 2024
The Big Feelings of the Sugar Apple Fairy Tale Anime05 julho 2024 -
 Monkeypox Case Is Discovered in Texas - The New York Times05 julho 2024
Monkeypox Case Is Discovered in Texas - The New York Times05 julho 2024 -
 Castlevania: Lords of Shadow 2 - IGN05 julho 2024
Castlevania: Lords of Shadow 2 - IGN05 julho 2024 -
 Lata com Cartas Pokémon Summer Tin 2023 EN - Miraidon05 julho 2024
Lata com Cartas Pokémon Summer Tin 2023 EN - Miraidon05 julho 2024 -
 Samsung Galaxy A14, Samsung Galaxy M54 5G, and more leak online - India Today05 julho 2024
Samsung Galaxy A14, Samsung Galaxy M54 5G, and more leak online - India Today05 julho 2024 -
 Pokemon Black and White Starter Perlers by jrfromdallas on DeviantArt05 julho 2024
Pokemon Black and White Starter Perlers by jrfromdallas on DeviantArt05 julho 2024